If your Windows PC is not working properly and you want to troubleshoot or send the running processes list to your local administrator to solve problems, exporting the running processes to Windows 10/8/7 may be handy. Once you export a list of running apps in a text file, even you can take a printout for any reason.
You can generate a list of running apps in Windows 10/8/7, even if your Task Manager is not accessible as well. Usually, the Task Manager program is used to view running processes with memory usage and PID, where you can instantly kill any task/process.
Most stubborn viruses create a new entry in the Service Manager and disable the services.msc and even Task Manager. That means troubleshooting gets difficult for an average user.
This post will learn to generate a text file of running processes with PID and memory usage in Windows 10/8/7. With the help of this method, you can get a fair idea about the background activity of your Windows system.
How to dump a text file list of running processes in Windows 10/8/7?
To generate a list of the running processes in the Windows operating system, perform the following steps:-
Step 1. Open the command prompt with admin rights. (To open the Command Prompt window with admin right, press the Windows logo + R keys to open the Run dialog box. Type cmd and hit Ctrl + Shift + Enter from the keyboard.)
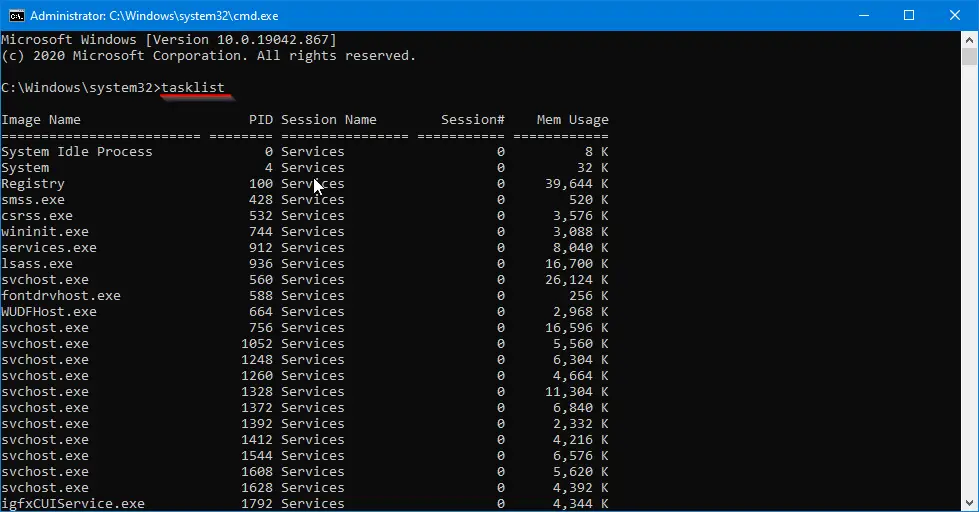
tasklist
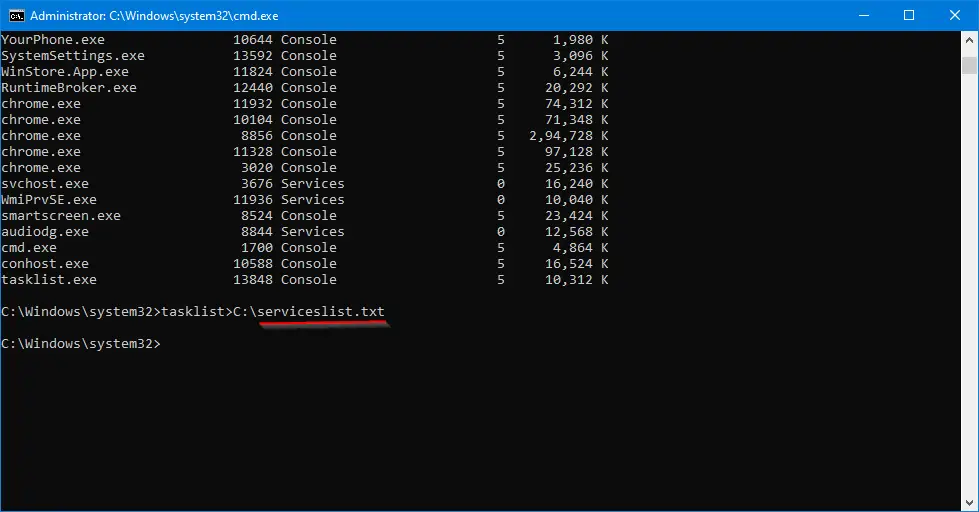
Step 4. To get the output of the running command in a text file, type the following and press Enter from the keyboard:-
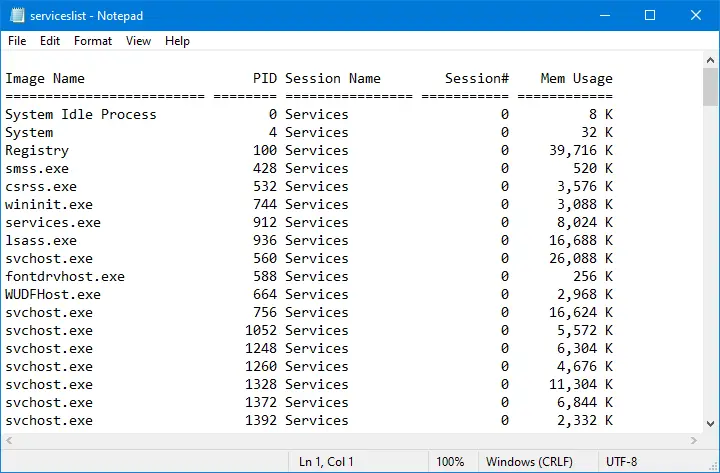
tasklist>C:\serviceslist.txt
Note: Above command will export running processes in “C:\serviceslist.txt”.If you want to get the output in another drive, change the drive letter “C” to any other.
Step 5. Once you execute the above command, a text file with serviceslist.txt will be generated under the “C” drive. You can open the file by double-clicking on it.
Note: You can even execute the command tasklist/svc>C:\processlist.txt to get services in the “C” drive. You can change “C” with any other letter to get the output in the desired drive.
Conclusion
In conclusion, troubleshooting problems on a Windows PC can sometimes require a list of running processes. While Task Manager is usually used for this purpose, some viruses can disable it, making it difficult to identify the cause of the problem. Thankfully, there is a way to generate a text file list of running processes with PID and memory usage in Windows 10/8/7. By following the simple steps outlined in this post, you can export the running processes to a text file and gain a better understanding of your system’s background activity. This information can be useful for troubleshooting problems and identifying any potential issues with your computer.