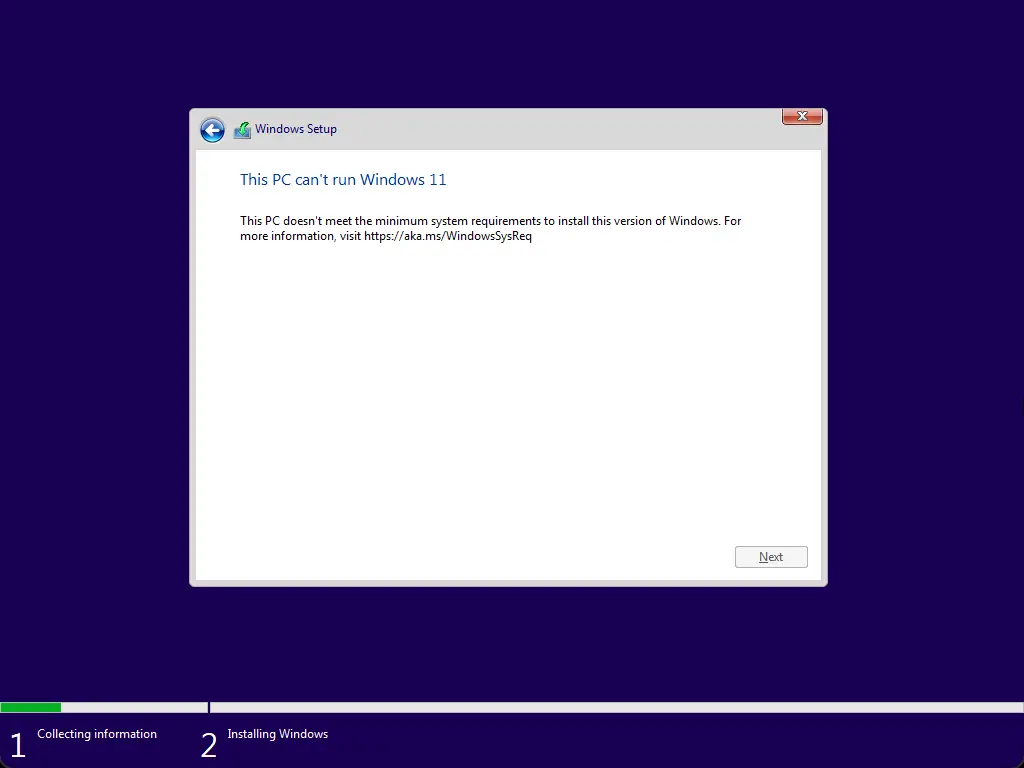
If you are trying to install Windows 11 on a VMware, VirtualBox, or physical machine and see the error, “This PC Can’t Run Windows 11,” this gearupwindows article will help you. If you see this error, that means your machine does not fulfill the Windows 11 installation requirements. For example, we failed when we tried to install Windows 11 on a VirtualBox with 2GB RAM, 2 Core CPUs, and a 60GB HDD configuration. Installation of Windows 11 failed with the message, “This PC Can’t Run Windows 11.”
Then, I bypassed the system requirements using Registry, and finally, I installed Windows 11 without TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot, even on 2GB RAM and 2 Core CPU hardware.
If you’re also struggling to install Windows 11 on unsupported hardware, you can get success installing Windows 11 on a virtual or physical machine without modifying the Windows 11 official ISO.
How to Fix the “This pc can’t run Windows 11” Error and install Windows 11 on Unsupported PCs?
The below-mentioned steps are applicable for all unsupported PCs, including VirtualBox or VMware, that do not meet the minimum hardware requirements to install Windows 11. Basically, in this gearupwindows article, we will guide you on bypassing RAM, CPU, SecureBoot, and TPM 2.0 and installing a new Windows 11 from scratch. Here are the steps:-
Step 1. First, download Windows 11 latest ISO from the Microsoft website.
Step 2. Then, start installing Windows 11 on your machine.
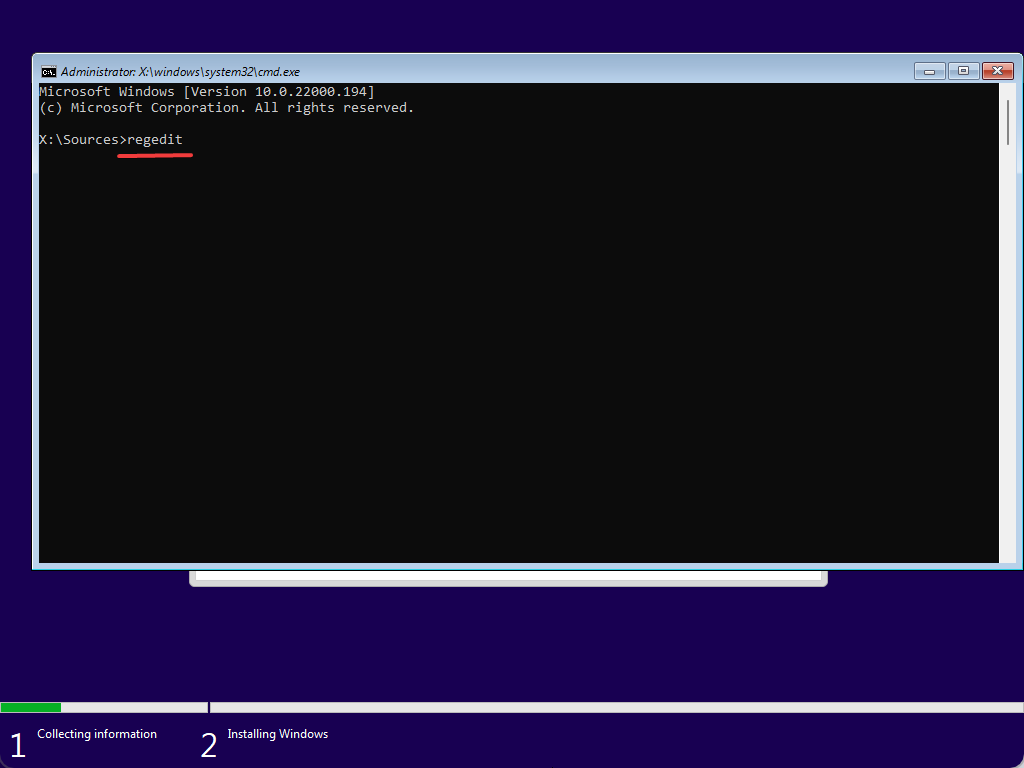
Step 3. When you see the error, “This PC can’t run Windows 11,” hit Shift + F10 (or Shift + Fn + F10) to open the Command Prompt.
Step 4. On the prompt, type regedit and hit Enter key on the keyboard to open the Registry Editor window.
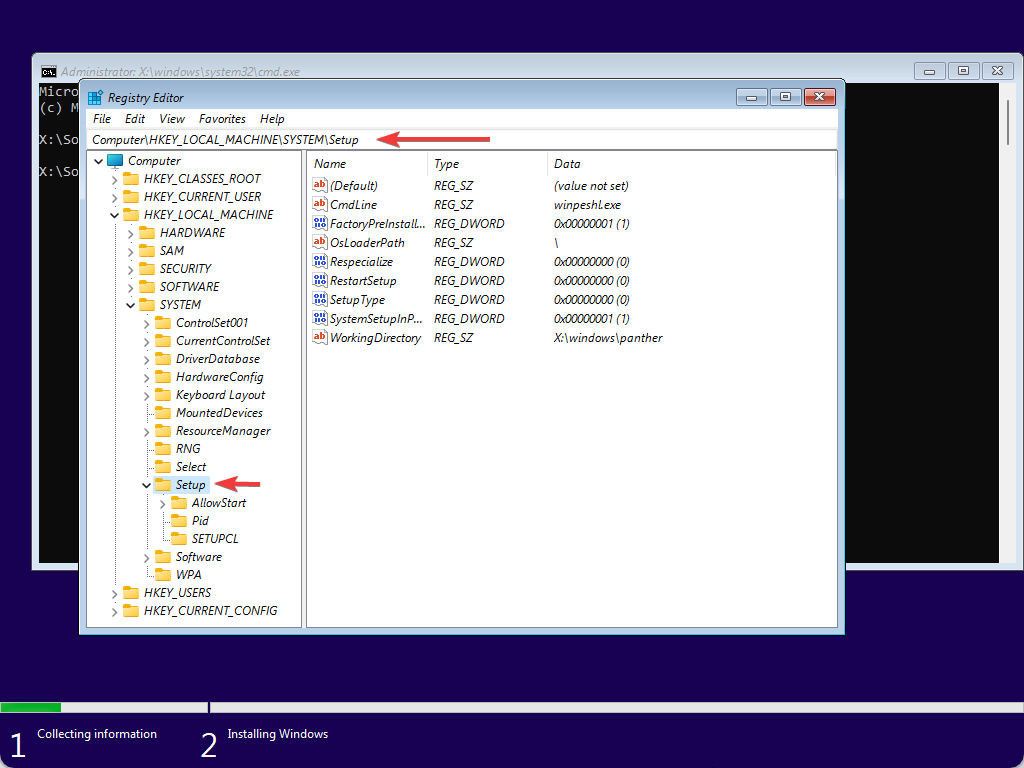
Step 5. When the Registry Editor window opens, navigate to the following key in the left sidebar:-
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\Setup
Step 6. Then, right-click on the Setup folder and select New > Key.
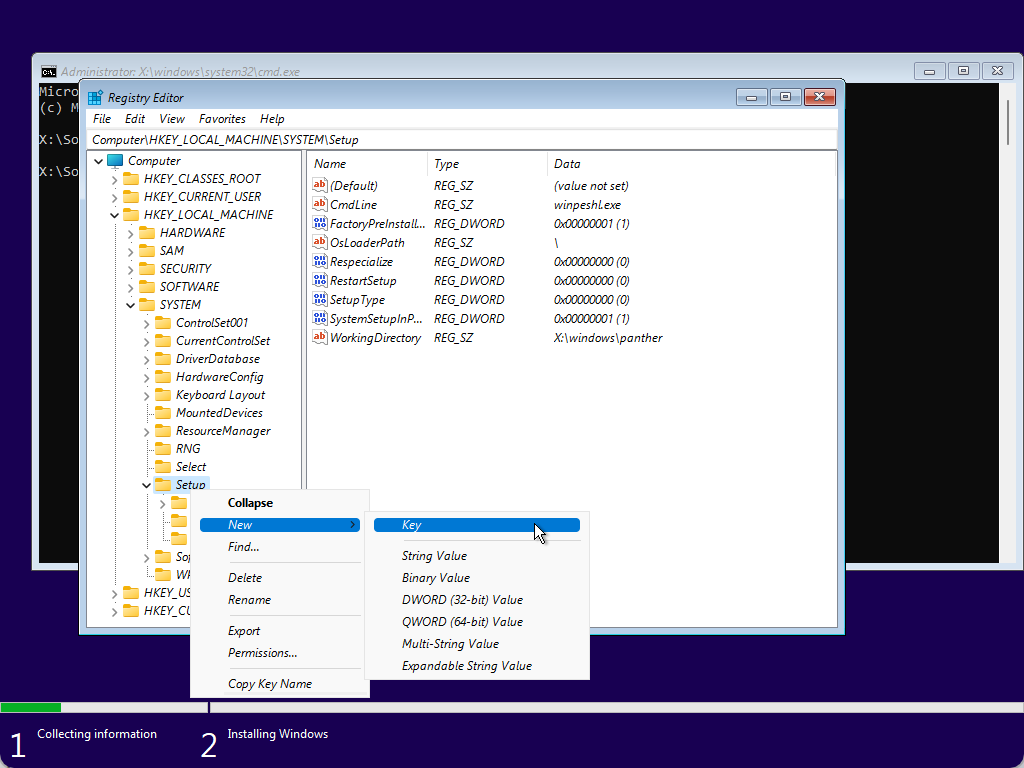
Step 7. After that, name the newly created key as LabConfig.
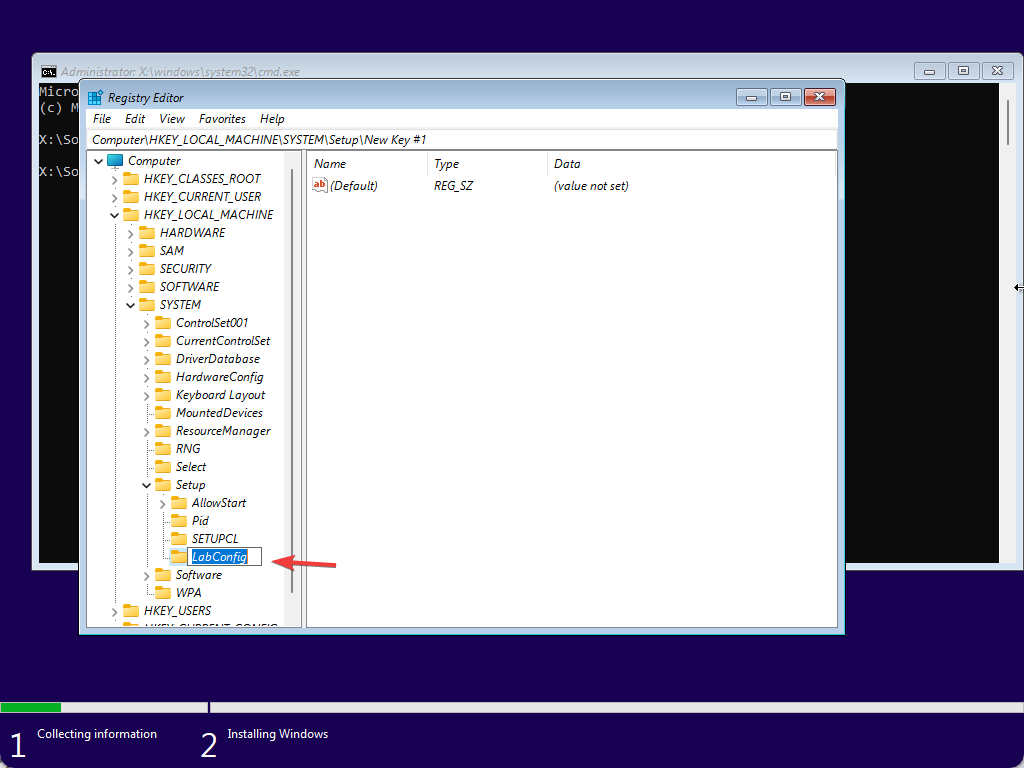
Step 8. Next, right-click on the LabConfig key and select New > DWORD (32-bit) Value.
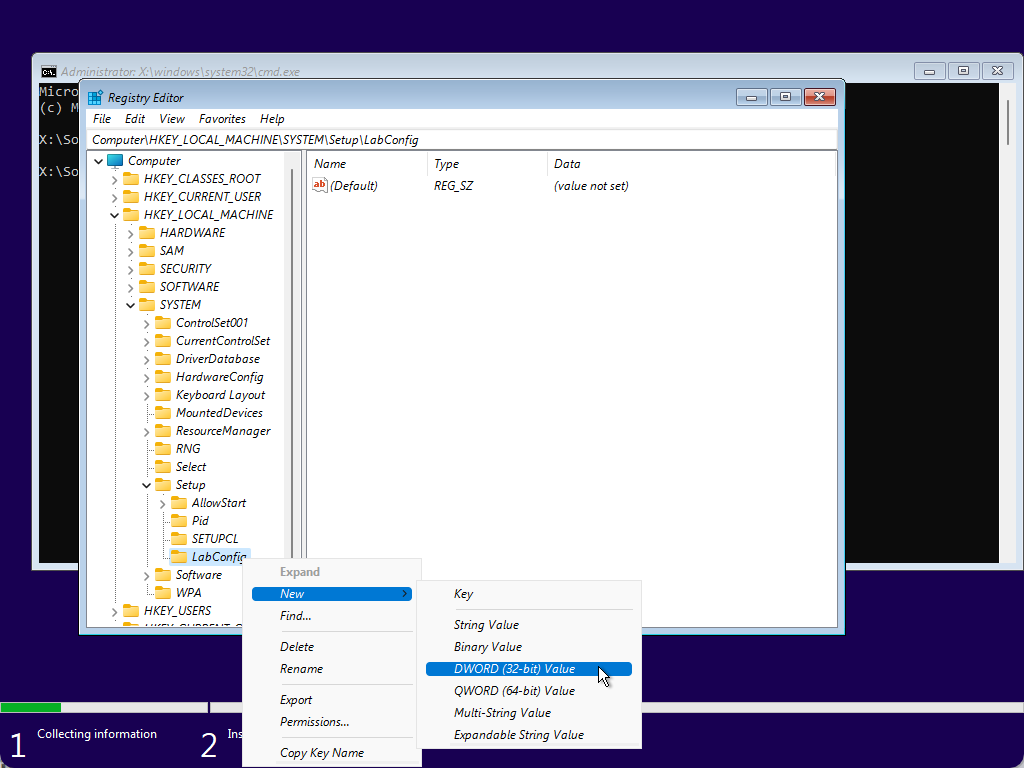
Step 9. After that, name it as BypassTPMCheck.
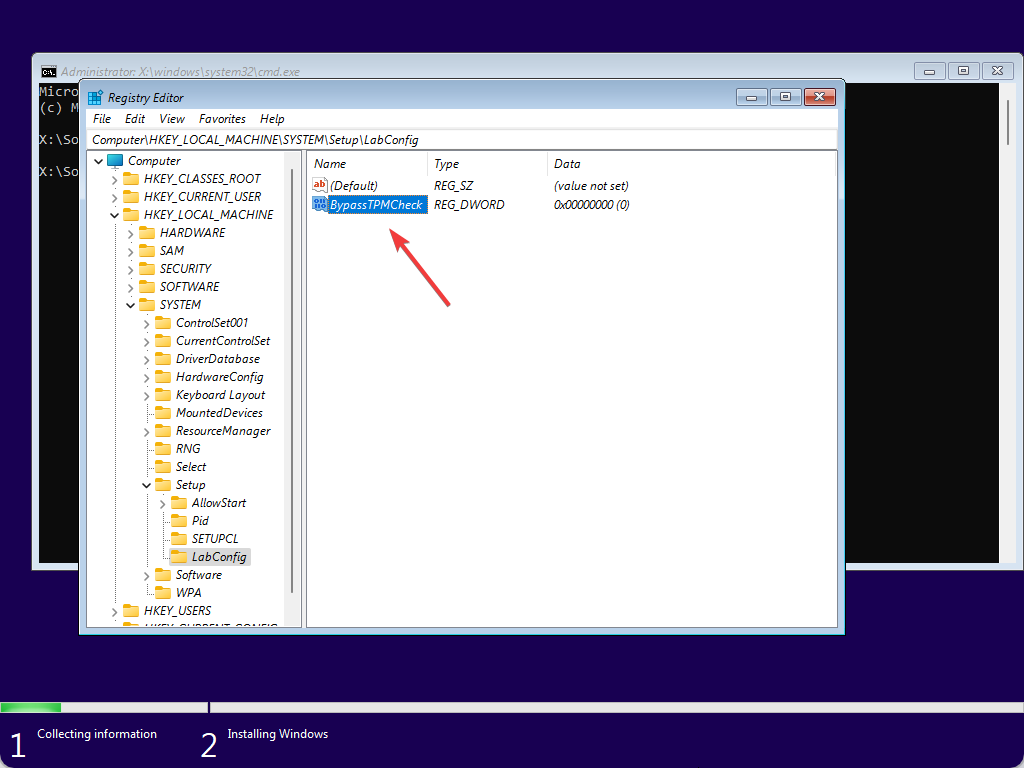
Step 10. Now, double-click on the BypassTPMCheck REG_DWORD and set its Value data to 1.
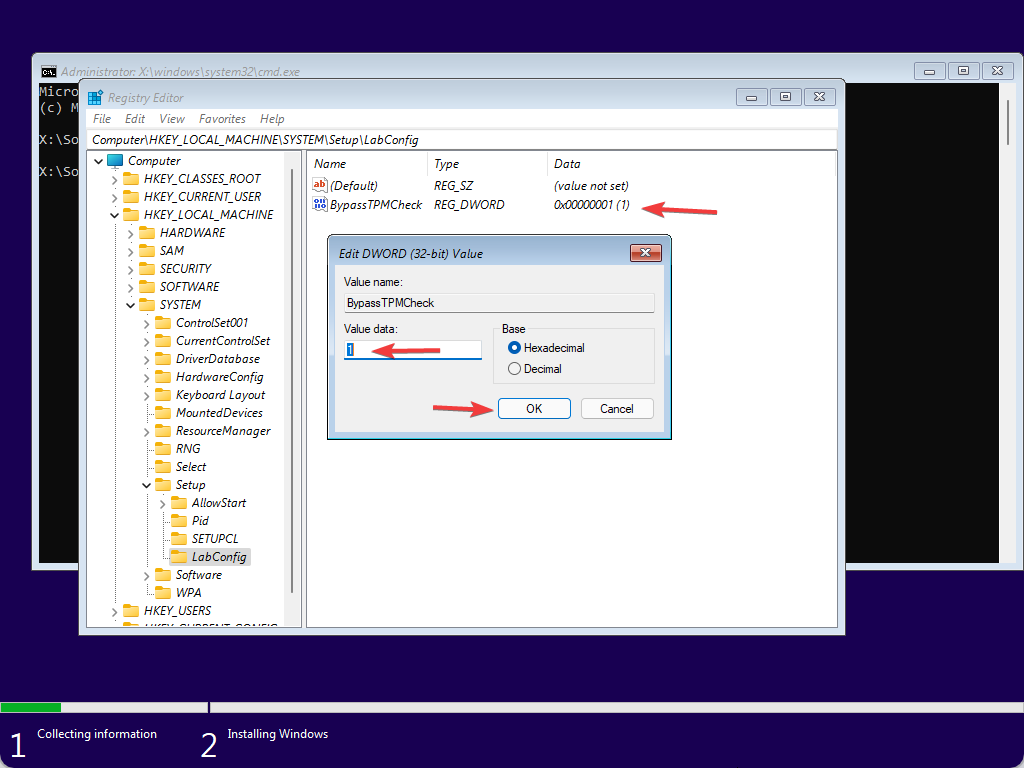
Step 11. Then, hit the OK button.
Step 12. To disable the Secure Boot Check, again right-click on the LabConfig folder and select New > DWORD (32-bit) Value. Name it as BypassSecureBootCheck and set its Value data to 1.
Step 13. Similarly, to bypass the RAM check, right-click the LabConfig folder and select New > DWORD (32-bit) Value. Name it BypassRAMCheck and set its Value data to 1.
Step 14. To bypass the CPU check, right-click on LabConfig and select New > DWORD (32-bit) Value. Name it BypassCPUCheck. Set its Value data to 1.
Step 15. Until now, you have bypassed Secure Boot, TPM, RAM, and CPU checks. Your registry should look like the below image:-
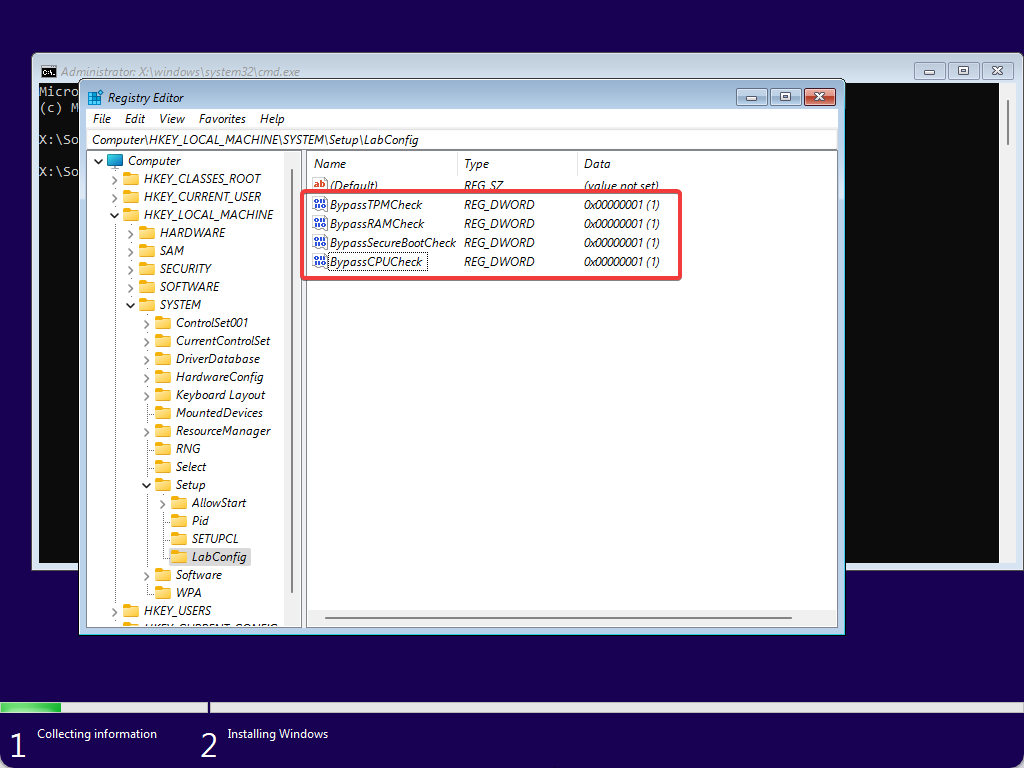
Step 16. Now, close the Registry Editor and Command Prompt windows.
Step 17. Then, close the Windows Setup window. Click the Yes button when prompted.
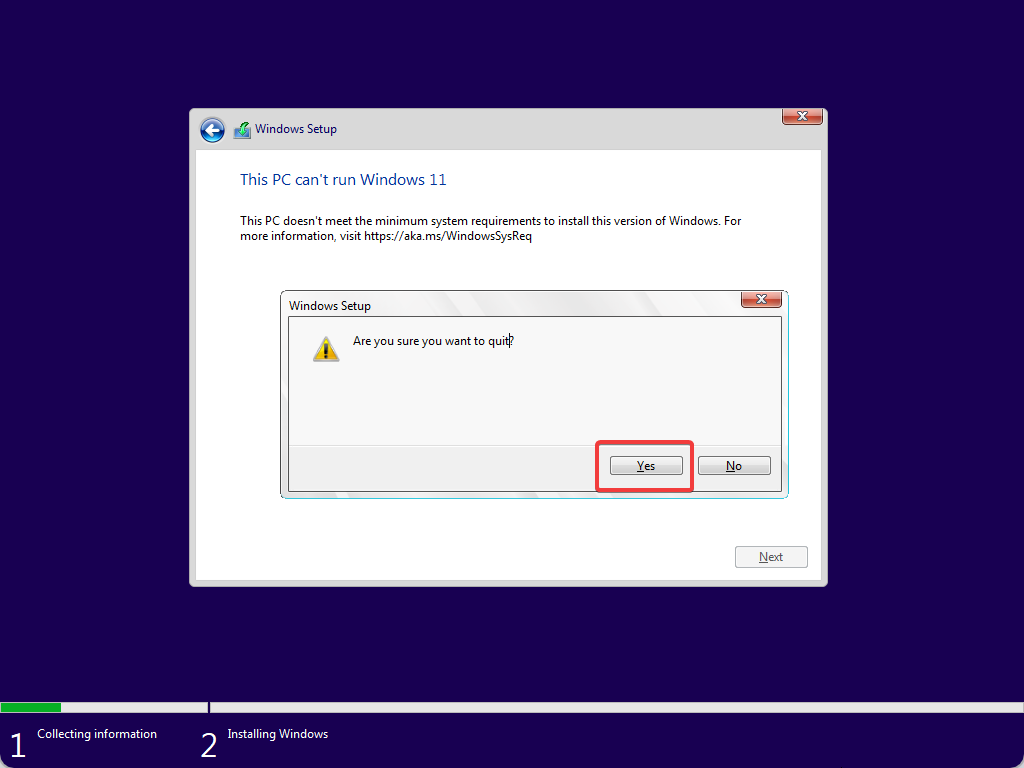
Note: Please don’t restart your computer. If you reboot your computer at this stage, you’ll need to repeat the above steps.
Step 18. Now, click the Install now button to start installing Windows 11 again.
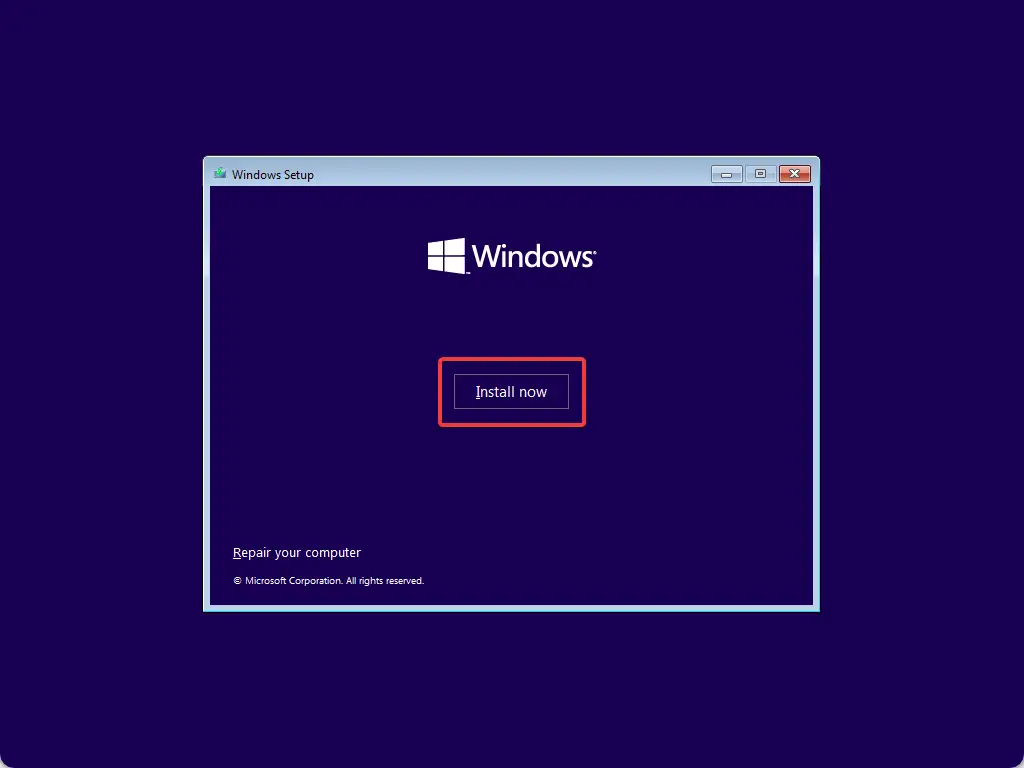
At this time, you’ll not get any errors. You can continue installing Windows 11 now without an error.
Conclusion
In conclusion, installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware can be a challenging task, especially when you encounter the error, “This PC can’t run Windows 11.” However, this gearupwindows article provides a helpful guide on how to bypass RAM, CPU, SecureBoot, and TPM 2.0 requirements and install Windows 11 on unsupported machines. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can successfully install Windows 11 without modifying the official ISO. It is important to note that bypassing system requirements may affect the performance and stability of Windows 11, so it is recommended to use the operating system on supported hardware.
Also Read: How to Install Windows 11 Home without Microsoft Account?