The Windows Registry is a crucial hierarchical database that stores low-level settings for the Microsoft Windows operating system and various applications. It serves as a foundation for the kernel, device drivers, services, Security Accounts Manager, and user interface. The Windows operating system heavily depends on it. The Registry holds all the settings, options, and values for installed programs and hardware. Whenever a program runs, it often accesses the Registry to function properly.
It’s important to note that if the Registry becomes corrupt, it may cause Windows to malfunction. Therefore, it’s essential to back up the Registry before making any changes.
In this gearupwindows guide, we’ll show you how to create a backup and restore Registry keys on Windows 11/10/8/7. A Registry backup is crucial because it allows you to revert to the original state if something goes wrong. You can either take a full backup of the Registry or back up individual keys.
How to back up the whole Registry on Windows 11/10/8/7?
Follow these steps to back up the entire Registry:
Step 1. Press the Windows logo + R keys to open the Run dialog box.
Step 2. Type regedit.
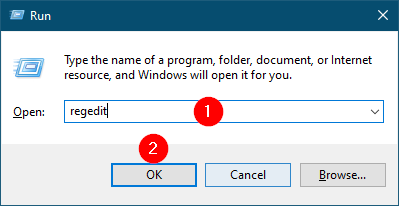
Step 3. Click the OK button.
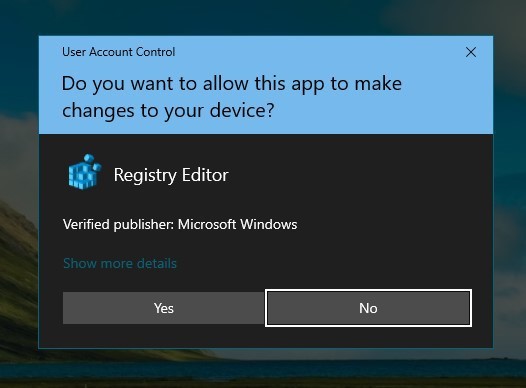
Step 4. If UAC (User Account Control) prompts, click Yes.
Step 5. In Registry Editor, click File > Export.
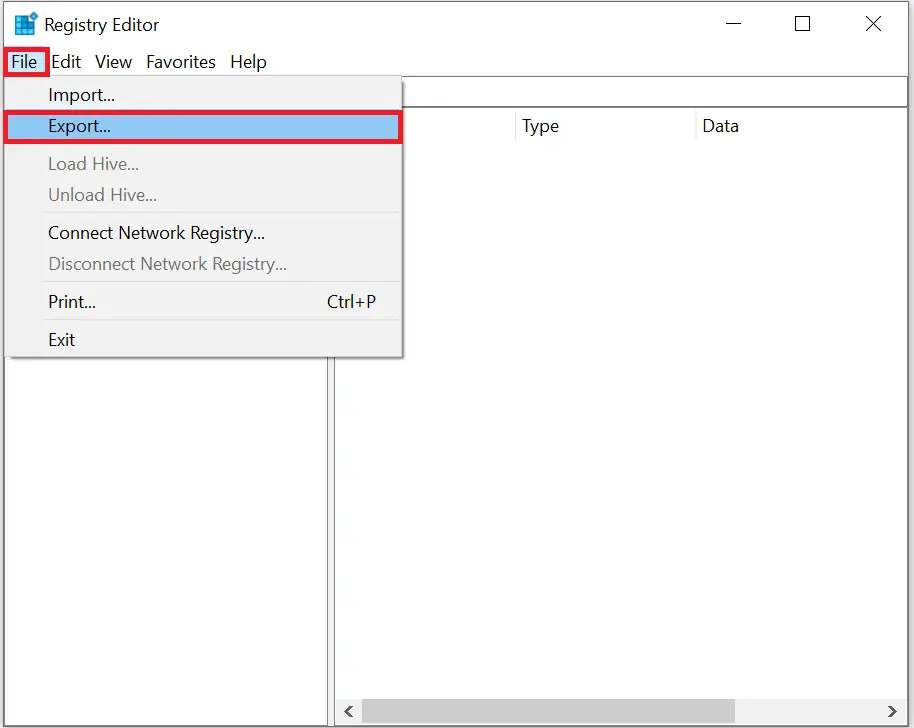
Step 6. Choose a location, enter a name (e.g., Full Registry Backup), and ensure the Export range is set to All.
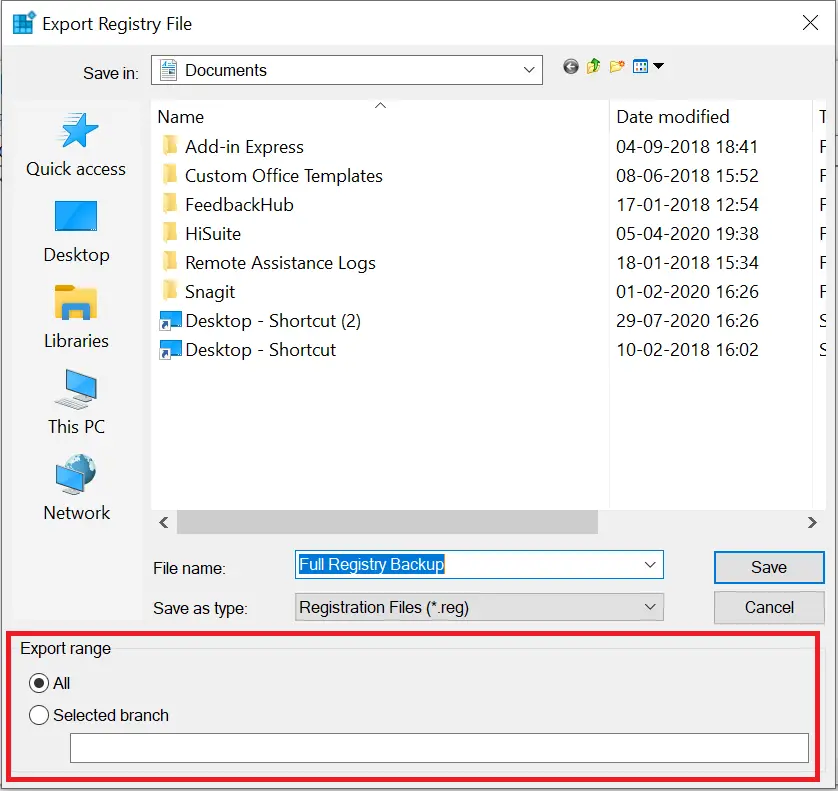
Step 7. Click the Save button.
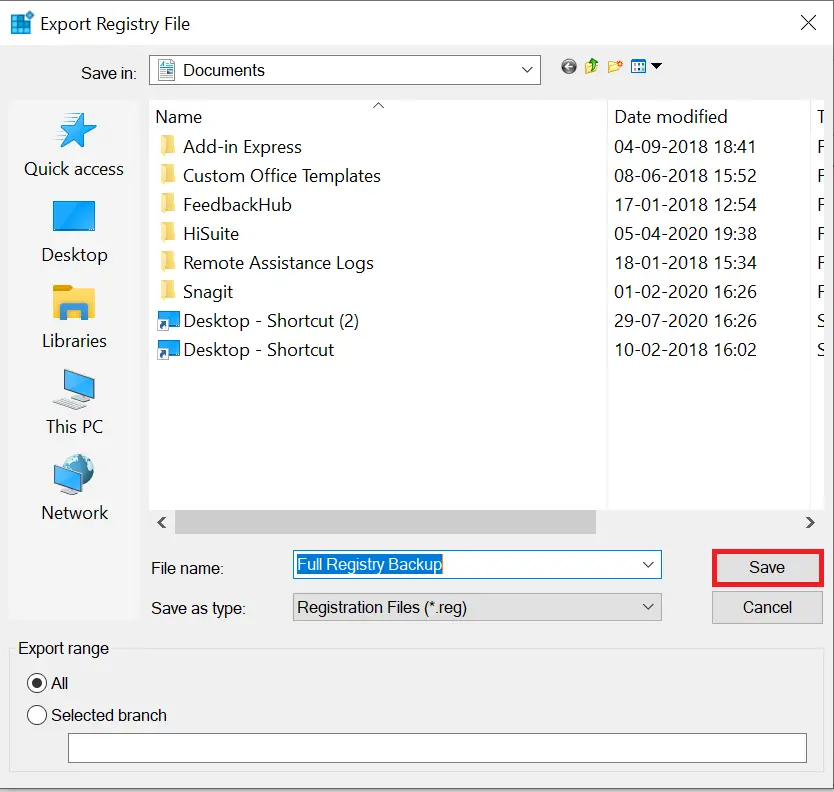
Depending on the Registry size, the backup process may take a few seconds.
How to restore the complete Registry on Windows 11/10/8/7?
If you’ve made changes and need to revert to a backup:
Step 1. Press Windows logo + R.
Step 2. Type regedit and click OK.

Step 3. If prompted by UAC, click Yes.


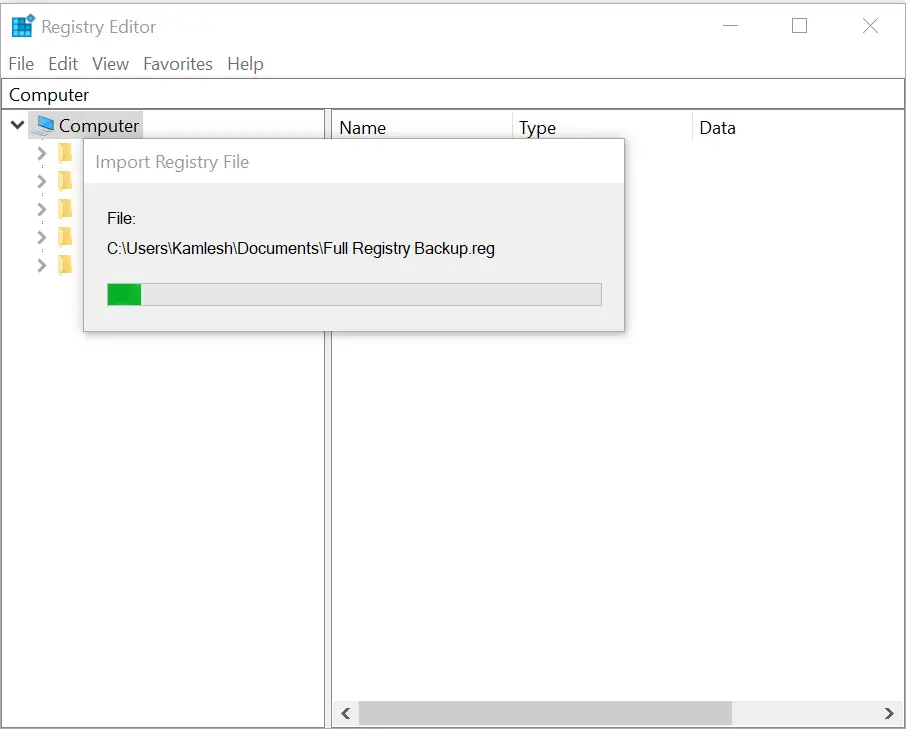
Step 4. Go to File > Import.
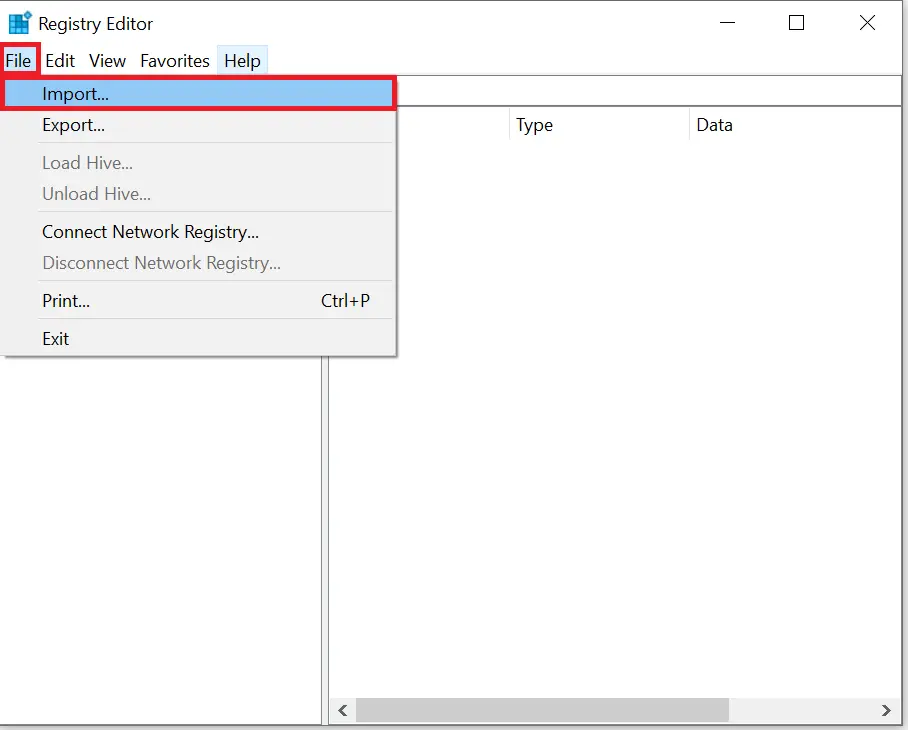
Step 5. Locate your backup file and click Open.
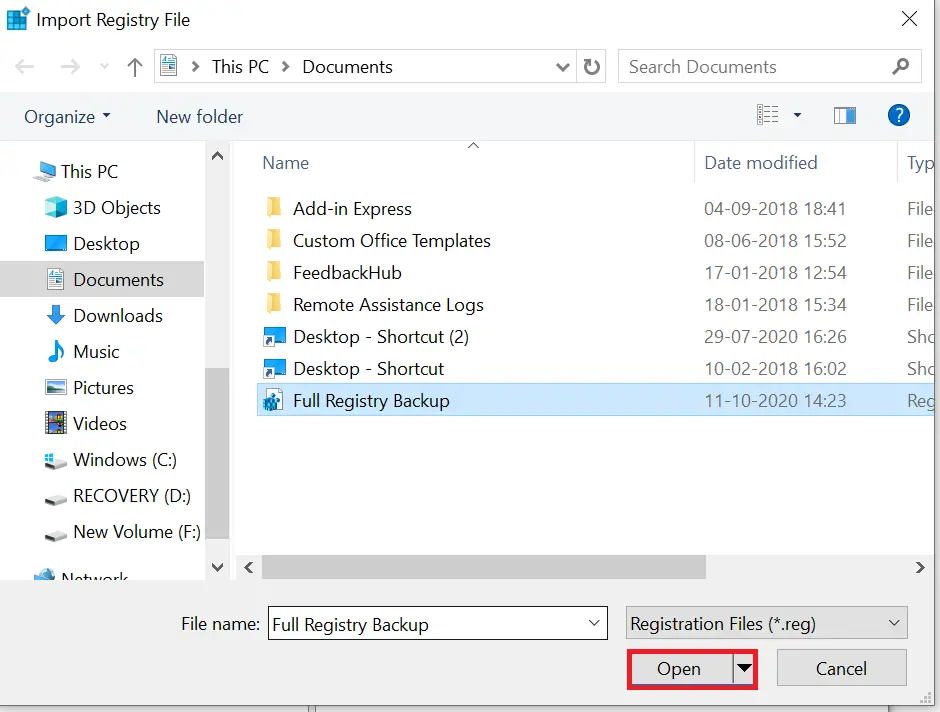
You’ll see the progress of the import.
How to back up individual Registry keys on Windows 11/10/8/7?
To back up specific keys:
Step 1. Press Windows logo + R and type regedit.
Step 2. Click OK and approve the UAC prompt if asked.

Step 3. Navigate to the key you want to back up – for example, see details on how to disable USB or CD drives via Registry.
Step 4. Click File > Export.
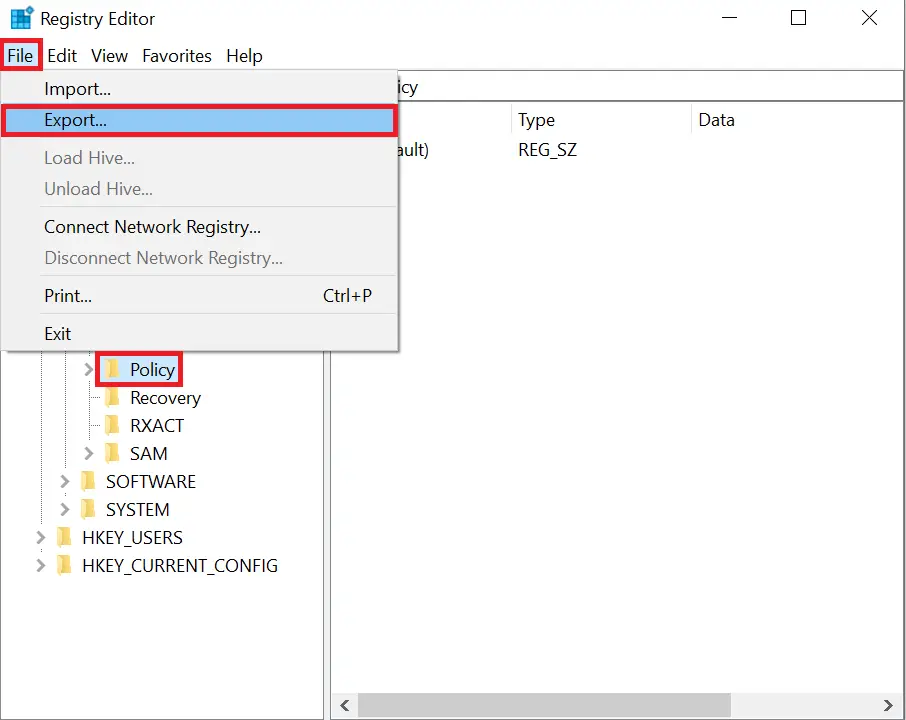
Step 5. Choose a filename and ensure Export range is set to Selected branch.
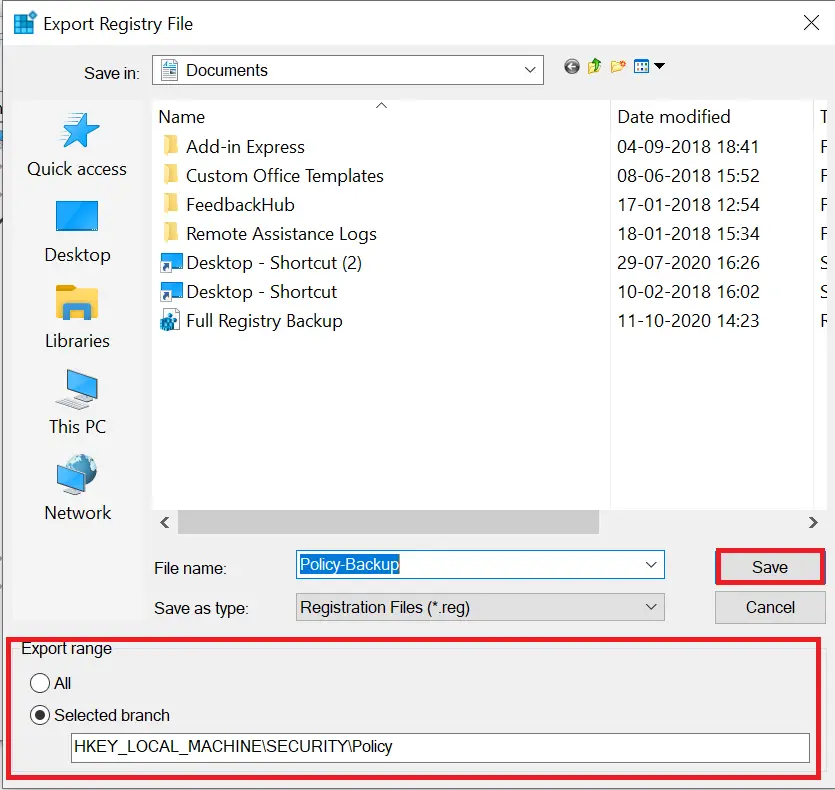
Step 6. Click Save.
How to restore individual Registry keys on Windows 11/10/8/7?
To restore a specific key:
Step 1. Open regedit from the Run dialog.
Step 2. Approve the UAC prompt.

Step 3. Go to File > Import.

Step 4. Select the backup file and click Open.
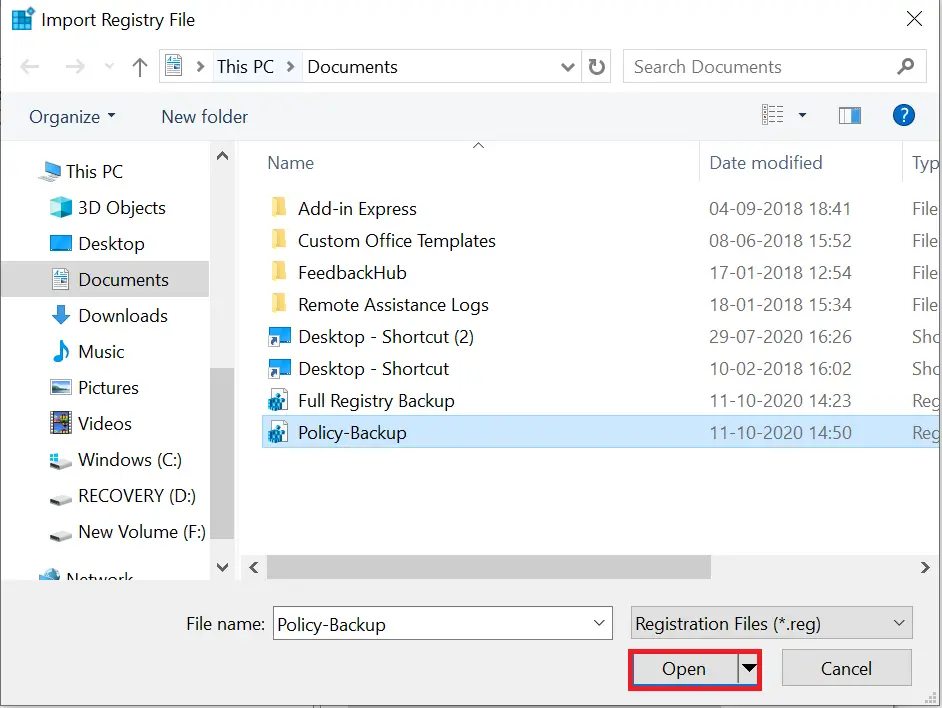
Step 5. You’ll see the confirmation: “The keys and values contained in [filename].reg have been successfully added to the registry.”
Frequently Asked Questions About Windows Registry Backup
Is it necessary to back up the Registry before editing?
Yes. The Registry is sensitive, and even small errors can cause Windows to malfunction. Always create a backup before making any manual changes.
Where is the Windows Registry stored?
The Registry is stored in multiple files inside the C:\Windows\System32\Config\ folder and in hidden user profile files. However, editing them directly is not recommended.
Can I use tools to automate Registry backups?
Yes. You can enable scheduled Registry backups using our guide on automatic Registry backup in Windows 11/10. For most users, the built-in Export/Import method outlined above remains the simplest approach.
Can I restore a Registry backup in Safe Mode?
Yes, you can launch regedit in Safe Mode and import a backup file if Windows is not booting properly due to Registry errors.
What’s the difference between a full Registry backup and System Restore?
A full Registry backup only saves Registry data, while System Restore creates a snapshot of system files, drivers, Registry, and settings. For maximum safety, use both.
Conclusion
The Registry is vital to Windows’ operation. Backing it up—fully or key-specific—before editing helps prevent serious issues. This article walks through both full and partial backup and restore steps for Windows 11/10/8/7.
For extra security tweaks, read how to reset virtual memory via Registry or how to disable the Open File security warning. Keeping backups ensures you always have a fallback.
